Unveiling Sexually Transmitted Diseases: Demystification of 6 Terrifying STDs
Sexually transmitted diseases

Sexually transmitted diseases have intense impact on human sexual and reproductive life. Sexually transmitted disease could be spread through bacteria, virus or parasites and almost 30 types of pathogens have potential to cause it. Sexually transmitted diseases are known to be transferred through sexual contact oral sex, anal or vaginal. Every year around 374 million people encounter any of the curable (Chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis and trichomoniasis) sexually transmitted diseases.
It is surprising that every day around 1 million sexually transmitted diseases affect people by remaining asymptomatic. Around 500 million people around the world are affected by genital infections with symptoms of herpes simplex virus in between an age group of 15-49 years.
Under the context of sexually transmitted disease, there are 8 known pathogens out of which 4 (syphilis, gonorrhea, Chlamydia and trichomoniasis) are curable while other (Herpes, simplex virus. HIV, hepatitis and human papillomavirus) are incurable.
However, there are some other sexually transmitted infections are lethal i.e. monkey pox, Zika, Ebola, Shigella Sonnei, Neisseria Meningitidis and other re-emerged infection lymphgranuloma veneruem. The emergence of such infections not only affecting people but also pose serious challenges to address in timely fashion.
Sexually transmitted diseases not only affect overall health but halt sexual and reproductive health as well. These STIs are associated with infertilities, cancers, stigmatization and complications in pregnancies. Drug resistance is also another challenge to curb its adversities. Human papillomavirus (HPV) cause around 311000 cervical cancers annually. In 2016, around 1 million women encountered syphilis.
What risks are linked with sexually transmitted diseases?
According to WHO, in 2020 around 374 million sexually transmitted infections attacks the globe i.e. Syphilis accounted for 7.1 million, Chlamydia made 129 million, gonorrhea make 82 million and trichomoniasis accounted for 156 million. Furthermore, as per estimates around 296 million people are facing hepatitis B infection around the world.
Sexually transmitted diseases (STIs) have an extended impact than just an infection like:
- Human papillomavirus cause cervical as well as other cancer.
- The STIs transferred from mother to child have a potential threat of neonatal death, sepsis, still birth, neonatal conjunctivitis, low birth weight and congenital deformities.
- HIV occurrence increases manifolds due to gonorrhea, herpes and syphilis.
- Gonorrhea and Chlamydia cause infertility in women.
In 2019, hepatitis B results in 820000 deaths due to hepatocellular carcinoma and cirrhosis.
What are sexually transmitted diseases?
In order to pour more light on sexually transmitted diseases, here are some descriptions of STIs. The most common and fearful diseases are as follows:
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus)
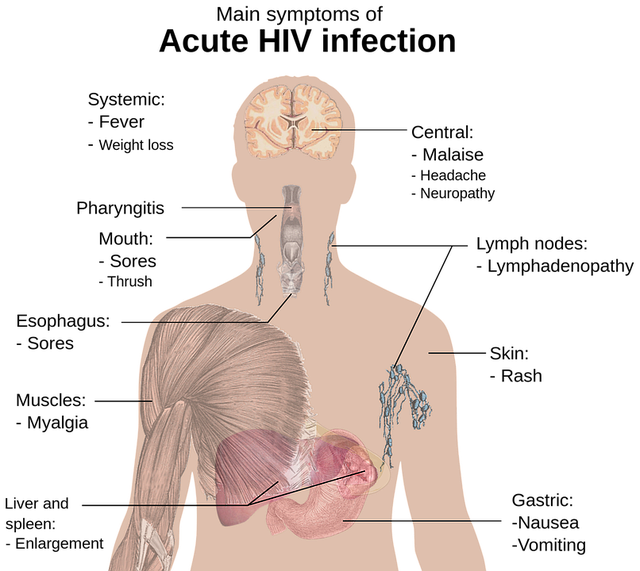
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is a specific virus which attacks on immune system. If unaddressed and untreated it may leads towards AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome). Unfortunately, till now there is no cure of it. But, it is controllable through medicines owing to which HIV patients could live a normal and happy life. It is considered a most lethal sexually transmitted disease.
HIV virus came from a breed of chimpanzees in Africa. Its roots are connected to late 1800s when human hunted chimpanzees and eat their meat. Due to infected blood and meat it spread slowly. The name of the derived virus is Simian Immunodeficiency Virus. The virus is also exists in US since 1970s.
As far as, the symptoms of HIV are concerned they are:
- Flu like symptoms which may be extends for several days or weeks.
- But, having flu like symptoms doesn’t guarantee the occurrence of HIV because flu happens due to multiple other infections as well.
- Some people may not even have any symptom and can be diagnosed through tests.
HIV progresses in stages. There are basically 3 stages if HIV not treated. But, it is rare nowadays of progression of HIV to AIDS (3rd stage).
Acute HIV Infection: Stage 1
It has flu like symptoms. At this stage the HIV virus is contained by the body in larger quantity in blood streams and poses serious threats to partner as well because it is contagious.
Chronic HIV Infection: Stage 2
This stage is categorized as clinical latency or HIV asymptomatic infection. At this stage the infection exist inside the body and replicate, people may not have any symptom but may spread virus. If treated timely this stage may not progress further to next stage but if untreated it may exceed to AIDS which is last and 3rd stage of infection.
It is serious stage of infection because if untreated it may increase viral load drastically and transform HIV to AIDS. Once infected with AIDS, people have sufficiently high viral load and capable to infect anyone. Without getting HIV treatment people with AIDS may live up to 3 years.
What are protective measures against HIV/AIDS?
The timely treatment is inevitable in case of HIV to avoid further spread. As it is contagious than while intercourse condoms should be used otherwise due to ample viral load infection may be transferred from one patient to other person.
The rapid test of HIV infection is present and could be used in case of extended flu like symptoms. Apart from all this, behavioral modeling is also really important to stay away from such deadly infections.
Chlamydia
Chlamydia is one of the sexually transmitted diseases which is more common in sexually active people and it’s also treatable. It can affect men and women. It has ample capacity to damage women reproductive system permanently. It may present severe difficulty in getting pregnant. It can also cause ectopic pregnancy.
Chlamydia is spread through anal, oral or vaginal sex with infected person even if male didn’t ejaculate. A pregnant lady may transmit infection to baby as well.
How to minimize risk of Chlamydia infection?
The only way to avoid this sexually transmitted disease is to avoid any type of sex. If anyone is sexually active then one must follow the following:
- Use condoms every time
- Maintain a long term monogamous relationship with a partner who hasn’t carry infection.
- The gay or bisexual people are also at risk.
One must get tested for Chlamydia if:
- Less than 25 years age
- If your partner is infected from Chlamydia or any sexually transmitted disease.
- If you have multiple sex partners.
If a woman is infected from Chlamydia then there are optimum chances of spreading infection to baby. It may results in eye infection or pneumonia in baby. Therefore, testing and diagnosing are really important.
What are symptoms of Chlamydia?
The symptoms may or may not be present in case of Chlamydia. They may erupt after several days or even after several weeks of intercourse. However, some symptoms among women may be:
- Abnormal vaginal secretions or discharge
- Feel of burning while peeing
Among males following symptoms may be present:
- Penis discharge
- Burning while peeing
- Pain in testicles
One noteworthy fact is that both male and females may get Chlamydia in rectum as well due to anal sex. It may have following symptoms:
- Pain in rectum
- Discharge and bleeding
If having such symptoms one must seek guidance from concerned medical practitioner. Urine test or vaginal swab tests may be used to diagnose infection.
Chlamydia is treatable and curable. One must re test for it after successful treatment because recurrence is normal.
The medicines used while treatment may cure it but the damage already incurred cannot be reversed. It may also take into consideration that if someone did get single dose of medicine must wait for at last 7 days.
Gonorrhea
It is one of the sexually transmitted diseases which is basically caused by a bacteria named as Neisseria Gonorrhoeae. It mainly causes infection in fallopian tube, cervix and uterus. However, it also infects urethra in males and females as well. It has capacity to infect mucous membranes of eyes, rectum, throat and mouth.
Is Gonorrhea a common disease?
Yes, it is a common infectious disease. Gonorrhea is considered as an infection which is one of really common sexually transmitted diseases. Around 1.6 million cases happened in 2018 mostly among young people around 15-24 years of age. Actually, due to asymptomatic nature of STDs most of burden of them remain overlooked.
How gonorrhea infections transmit?
It is transmitted through sexual contact via vagina, mouth, anus and penis of a person already having infection. For transmission of it ejaculation is not mandatory and it can also spread through mother-child transfer.
Someone who got treatment of gonorrhea may also if contacted by infected person.
Mostly, young, adults, teenagers and African Americans are found infected due to hyper sexually activation.
What are signs and symptoms of gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea is normally asymptomatic. Signs and symptoms of infection in urethra among males include white, yellow or green discharge or dysuria. The discharge commonly happens between 1-14 days of infection. In chronic condition like epididymitis, men complaint about pain in scrotum or testicles.
Among women, it is also asymptomatic and even so mild that females consider it vaginal or mild bladder infection. The symptoms among women include dysuria, bleeding from vagina or vaginal discharge. Women gonorrhea has tendency to present serious complications.
Furthermore, the infection in rectum among both male and females show signs like bleeding, painful bowel movement, itching and soreness. Rectal infection is also asymptomatic.
What are complications of gonorrhea?
The timely addresser and treatment of gonorrhea is really important otherwise it poses serious health problems like other sexually transmitted diseases. Among women, gonorrhea may spread through fallopian tube and uterus which results in pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). Symptoms may vary from mild to severe and may cause fever and abdominal pain. PID results in internal pelvic pains and abscess. PID can also permanently damage fallopian tubes which cause infertility and increase threat of ectopic pregnancy.
On the other part, among men, gonorrhea further complicates the condition by epididymitis. In rare instances, infertility may happen as well.
If gonorrhea remains untreated it could penetrate in blood cells and cause gonococcal infection (DGI). It can be life threatening and cause dermatitis, arthritis and tenosynovitis.
Most importantly, it is noteworthy that if gonorrhea is untreated it may acquire or transmit HIV virus which cause AIDS.
It is recommended to test for gonorrhea for sexually active male and females less than 25 years of age to diagnose this sexually transmitted diseases.
In addition to all this, one must note that urogenital gonorrhea can be tested and diagnosed through urine tests or through vaginal, urethral or endocervical samples by using nucleic acid amplification (NAAT) or through gonorrhea culture.
Syphilis
Syphilis is one of the sexually transmitted diseases which poses serious health problems if it remains untreated. It happens in four stages and each stage has its own signs and symptoms. It spreads through direct contact with a syphilis sore while oral, anal or vaginal sex. A pregnant mother can also spread it to unborn baby.

What are risk factors of syphilis?
Syphilis could be spread through unprotected oral, anal or vaginal sex or through sex without condoms or sex with already infected person. It is one of the severe sexually transmitted diseases.
The regular testing of gay, bisexual, HIV patient, a person with positive syphilis infection is mandatory. The pregnant women should get syphilis test during her first prenatal visit. Few people are also recommended to undergo syphilis testing while third trimester at 28 weeks or at the time of delivery.
If a pregnant lady is exposed to syphilis she must take timely treatment to save child. Otherwise still birth, low weight baby and other problems may incur. Treatment of positive case during pregnancy is beneficial because untreated mother may cause baby diseases like cataracts, seizures, deafness and even death irrespective of signs or symptoms.
What are stages of Syphilis?
There are 4 stages of syphilis which are as follows:
Primary Stage
Primary stage characterized by single or multiple sores. Sores are basically the locations from where syphilis entered. Such sores may be present in, around or on:
- Anus
- Penis
- Rectum
- Vagina
- Lips
- Mouth
The sores are mostly painless that’s why most of time remain unnoticed. There remain active for 3-6 weeks and heal up but it is highly recommended to get timely treatment to stop transforming primary stage into next stage.
Secondary Stage
This stage is characterized by skin sores / rash in vagina, anus or mouth. This rash happens after healing primary sores or even after few weeks. This rash may also be on palms of hands and bottom sides of feet and they look
- Red or brownish red
- Rough
The other symptoms may include:
- Hair loss in patches
- Headache
- Weight loss
- Lymph nodes swelling
- Sore throat
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Muscle ache
In the absence of proper treatment the infection ay switch towards next stage.
Latent Stage
This stage mostly has no sign or symptoms and the syphilis may continue to affect in longer run.
Tertiary Stage
It is really deadly stage of syphilis which starts to damage body organs. It may attack even after 10 to 30 years after exposure to syphilis infection. The body organs like brain, heart, nervous system and blood vessels may be damage and cause death.
Genital Herpes
Genital herpes is one of the sexually transmitted diseases which is really common and it is caused due to herpes simplex virus (HSV). It is spread due t skin to skin touch while intercourse. It may be asymptomatic in most of the cases while some people may exhibit symptoms like itching, pain, sores outside the mouth, genitals or anus.
There is no basic treatment of genital herpes and it may be recurrent as well. Medicines, however, may give some relief. It also assists in further spread. One must use condoms to avoid spread.
What are symptoms of Genital Herpes?
The patients of genital herpes may or may not have symptoms or really mild symptoms even in most of the cases patient may not know whether he has infection or not.
Normally, the symptoms arise after 2-12 days of exposure to herpes virus. The symptoms may include:
- Itching and pain on or around genitals.
- Presence of blisters around anus, mouth or genitals.
- Scabs like ulcer heal
- Pain while urination
- Painful ulcers
- Urethral discharge
- Vaginal discharge
Initially, one may have flu like symptoms like:
- Headache
- Fever
- Swelling in groin area lymph nodes
- Body pain
While confronting from herpes infection one may develop sores and if one scratch or rub that it may spread further. The sores may develop on or in different areas of the body like anus, buttocks, thighs, vulva, vagina, cervix, rectum, mouth, urethra, scrotum or penis.
Genital herpes may affect after sometime again due to recurrent nature of this infection. It is also known as Recurrent Outbreak or Recurrent Episodes. The infection may also warn before attack in shape of pain in genitals and pain in legs, buttocks or hips. The best thing is to consult the doctor right away and avoid further spread.
What are caused of herpes genitals?
Genital herpes is happen due to two virus types i.e. Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) and Herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2). The details of both of these viruses are as under:
Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 (HSV-2)
It is the most common reason of genital herpes. This virus may be present inside the blisters or ulcers or inside the fluid of ulcers, inside the moist linings of mouth and rectum or vagina.
Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 (HSV-1)
It is a virus which causes fever blisters and cold sores. People may infect themselves when they come to skin to skin touch with infected person. A person having virus in mouth tissues may spread it to the partner while oral sex.
However, it is observed that HSV-2 is more common than HSV-1 outbreak. Both of these viruses cannot live on room temperature therefore it cannot be spread from towel use but could be spread through using infected person’s glass or any silverware.
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
Human papillomavirus is a group of almost more than 100 viruses. It is one of the common sexually transmitted diseases. In some cases it may not show any sign symptom but in some others it may cause warts on genitals and even cancer. It basically attacks on skin.
What are symptoms of HPV?
In most of the cases it does not show any symptom but in other cases it cause lumps around penis, anus or vagina and cause pain.
How HPV spread?
Human papillomavirus may spread through skin to skin touch, oral, anal or vaginal sex or by using sex toys. It is really common but because of the fact that it do not show symptoms in most of the cases that’s why lot of the people may even not know that they are infected. It is not necessary to have sex for its spread which make it more deadly than other sexually transmitted diseases.
What are conditions associated with Human Papillomavirus?
In most of the cases HPV do not present any symptoms. But in some cases it may cause warts on genitals, cause certain changes in cells which ultimately lads towards cancers. It can cause anal cancer, vaginal cancer, cervical cancer, penile cancer and vulval cancer. In rare cases it can also cause neck and head cancer as well.
Conclusions
Sexually transmitted diseases are really common yet most of the times they remain unaddressed owing to the fact that most of the infections do not present sign or symptoms. However, these sexually transmitted diseasesmust be addressed timely because they may damage the reproductive systems and also cause severe diseases like HIV, AIDS and in some cases may lead towards cancers.
Therefore, the need of time is to address and treat these infections timely and seek suggestion and prescription from medical practitioner. Last but not the least exploit healthy and standardized ways of sex and avoid such means which may deteriorate health and well being.
FAQs
What are sexually transmitted diseases?
HIV/AIDS, gonorrhea, syphilis, chlamydia, herpes, HPV
Are STIs lethal?
Yes but most of them are treatable.
What are there basic precautions?
Safe sex and hygiene.






