UNDERSTANDING LYMPHADENITIS AND 3 EFFECTIVE TREATMENT APPROACHES
Lymphadenitis
Lymphadenitis, an inflammatory condition affecting the lymph nodes, can be caused by bacterial, viral, or fungal infections. Early diagnosis of Lymphadenitis is crucial for appropriate treatment to prevent complications.
According to the World Health Organization, lymphadenitis is a painful condition in which your body’s white blood cells are abnormally active and inflamed in one or more areas of your body.
Lymph nodes which are about 600 in human body are commonly found in armpits, groin and neck regions. Lymph nodes are basically glands. They contain fluids and white blood cells which help in fighting against diseases as defense system of body.
Lymphadenitis Types
Lymphadenitis has two major types which are as follows:
Generalized Lymphadenitis
It may happen due to certain disease or illness and may results in infection in two or more nodes. It usually spread when infection runs in blood streams.
Localized Lymphadenitis
Such type of the lymphadenitis happens when infection occurs in one or few nodes in nearby areas of infection like in tonsil infection leads towards neck area lymph nodes enlargement.
Lymphadenitis Causes
Lymphadenitis may happen due to viral infections, bacterial and fungal exposures. Viral infections may happen due to common colds which results in lymph nodes swelling. Apart from it, lymphadenitis may occur due to following reasons:
- Cancer
- Leukemia
- Lymphoma
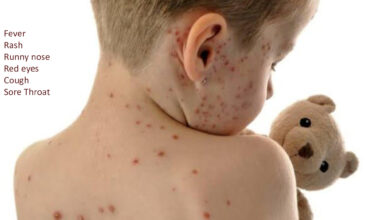
Lymphadenitis Symptoms
The symptoms of lymphadenitis include severe pain, swelling, stiffness, tenderness, and fever. It occur when your body’s immune system attacks the lining of the respiratory tract (tubitis) or other organs in the abdomen (peritonitis).
Symptoms may be mild but can quickly turn into serious complications if left untreated. For example, peritonitis can damage your esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and colon.
Lymphadenitis is usually caused by bacteria that enters your digestive system through a wound in your gut (ascites), such as from a urinary tract infection, surgery, or having an organ removed. In contrast, tubitis causes inflammation of the lining of your bowel (colitis), causing severe abdominal pains, diarrhea, and sometimes vomiting.
Commonly observed symptoms of lymphadenitis are as follows:
- Lymph nodes enlargement
- Pain in nodes
- Nodes may be soft or matted.
- Redness of nodes over the skin of lymph nodes
- Pus in nodes
- Flowing fluid out of the lymph nodes
- Upper respiratory tract infections like runny nose, fever and sore throat.
- Sweating in night
- Expansion and hardening of nodes which indicate the presence of tumors.
Lymphadenitis Diagnosis
It is diagnosed through physical examination. The health care provider may suggest undergoing several tests like:
- Blood tests
- Biopsy
- X-Rays
- CT Scans
Lymphadenitis Preventions
If you have been diagnosed with lymphadenitis and find it difficult to cope with the symptoms, there are several ways to prevent this problem.
- First, avoid foods that contain high levels of fat, such as fast food, sugary drinks, and alcohol.
- Second, limit your intake of proteins from red meat and chicken.
- Third, get plenty of fresh vegetables and fruits, especially those that contain a lot of fiber.
- Fourth, try to rest often, so your body gets enough sleep.
- Lastly, don’t forget about regular exercise!
However, there are several suggestions which definitely assist in preventing lymphadenitis.
- Try to consume as little fat as possible. High fat intake increases your risk for heart disease and obesity, which can cause weight gain and lead to it.
- Limit your intake of protein. A study has shown that people who eat too many proteins are at higher risk for developing it.
- Get plenty of vegetables. Studies have found that vegetables can reduce the severity of symptoms and slow down the progression of it.
- Stay up and have plenty of restful sleep. Sleeping on your back can help to keep things moving around in your body.
By following these tips, you can ensure that you don’t develop this condition.
It is crucial to note that some people may experience difficulty eating certain types of foods or beverages, which may also affect their ability to prevent it. If you feel like you’re getting sick, talk to your healthcare provider or dietitian about making changes to your diet and lifestyle. Additionally, it may be helpful to talk to a doctor or registered nurse about supplements and herbal medicine.
It may sometimes occur due to viral infections (such as colds). However, there is no cure for lymphadenitis. Here are some suggestions for fighting off the disease:
– Drink plenty of fluids. Drinking 8 glasses of water per day is recommended to help lower your risk for developing it.
– Avoid smoking. Smoking helps to exacerbate inflammation and increase the likelihood that you’ll get it.
– Exercise regularly. Physical activity is good for your physical health and can help to strengthen your immune system. Regularly doing exercises is also beneficial when it comes to preventing it. You can also incorporate yoga or meditation into your routine.
– Don’t smoke. Smoking increases your chance of developing an inflammatory condition called necrotizing enterocolitis, which is when small holes develop in the intestines. This can make it difficult to pass out.
– Take medication. If you have developed lymphadenitis and find that your symptoms seem to come and go without stopping, it may be time to take medications. There are many different types of drugs available that may help fight off lymphadenitis. Some examples include steroids, immunosuppressants, and other anti-inflammatory agents.
In addition to trying natural remedies, you may want to consider using over the counter medicines to combat the effects of infection. These products are available in most drugstores, including ones used to treat anxiety, depression, muscle spasms, and migraine headaches.
They are designed specifically to help alleviate symptoms of it, so they may offer relief for days at a time. Some popular ingredients include vitamins C, D, E, B6, folic acid, zinc, omega 3, etc.
It is important to remember that it is a real and debilitating medical issue that requires medical attention. By implementing all of the tips mentioned above, you can protect yourself and keep your family healthy.
With proper treatment and prevention, you can overcome symptoms and return to enjoying everyday activities. In the end, nothing lasts forever, but your loved ones can rest assured knowing that they are making the best decisions for them and their families.
Lymphadenitis Treatment
Antibiotics are commonly prescribed to target bacterial infections associated with it. Proper antibiotic selection based on the causative agent’s sensitivity profile is essential for a successful treatment outcome.
In cases of viral lymphadenitis, supportive care focuses on managing symptoms such as fever and pain. Antiviral medications may be considered in specific viral infections contributing to lymphadenitis.
Surgical intervention, such as lymph node drainage or biopsy, may be necessary for severe or recurrent cases of it. Surgery aims to remove infected or damaged lymph nodes to alleviate symptoms and prevent further complications.
Adjunct therapies like warm compresses and pain relievers can provide symptomatic relief for individuals with it. Proper wound care and hygiene practices are crucial to prevent secondary infections.
Conclusions
By understanding the underlying causes of lymphadenitis and tailoring treatment strategies accordingly are vital for managing this condition effectively. A multidisciplinary approach involving medical professionals can help optimize patient outcomes and quality of life.
In conclusion, it is important to pay attention to what you eat as well as how much you exercise. Eating healthily, exercising regularly, and staying socially connected will help to prevent it.
FAQs
What is lymphadentitis?
Lymphadenitis, an inflammatory condition affecting the lymph nodes, can be caused by bacterial, viral, or fungal infections.
What are causes of lymphadenitis?
Lymphadenitis may happen due to viral infections, bacterial and fungal exposures.
What are symptoms of lymphadenitis?
· Lymph nodes enlargement
· Pain in nodes
· Nodes may be soft or matted.
· Redness of nodes over the skin of lymph nodes
· Pus in nodes
· Flowing fluid out of the lymph nodes
· Upper respiratory tract infections like runny nose, fever and sore throat.
· Sweating in night
· Expansion and hardening of nodes which indicate the presence of tumors.






👍🏻👍🏻